
This course provides an introduction to basic neuroanatomy, the principles of neurophysiology and the stages of neuroembryological development. Neural systems will be introduced that contribute to sensory experiences, motor control, learning and memory. It also introduces selected neurological disorders

The goal of this course is to have the student develop and demonstrate a deeper understanding of the foundational principles of chiropractic as presented in 1PHIL1 and gain a practical appreciation of those concepts as they apply to the practice of chiropractic and health care in general.
- Teacher: Chris Ramsay

In a multicultural and diverse world, it is imperative to develop students’ understanding of and skills in communication, protocols and ethics underpinning successful professional communication for diverse cultures in NZ, in particular for Māori, in skills in te reo me ōna tikanga (language and custom), and to apply the cultural capability and belonging concepts to other cultural and diverse groups and situations.
This waananga series consists of 4 main stages, using the metaphor of starting in te pō, the night, the unknown towards te ao mārama, the world of light. This continuum of understanding is reflection also of the four stages of competence, moving from unconscious incompetence towards conscious competence.
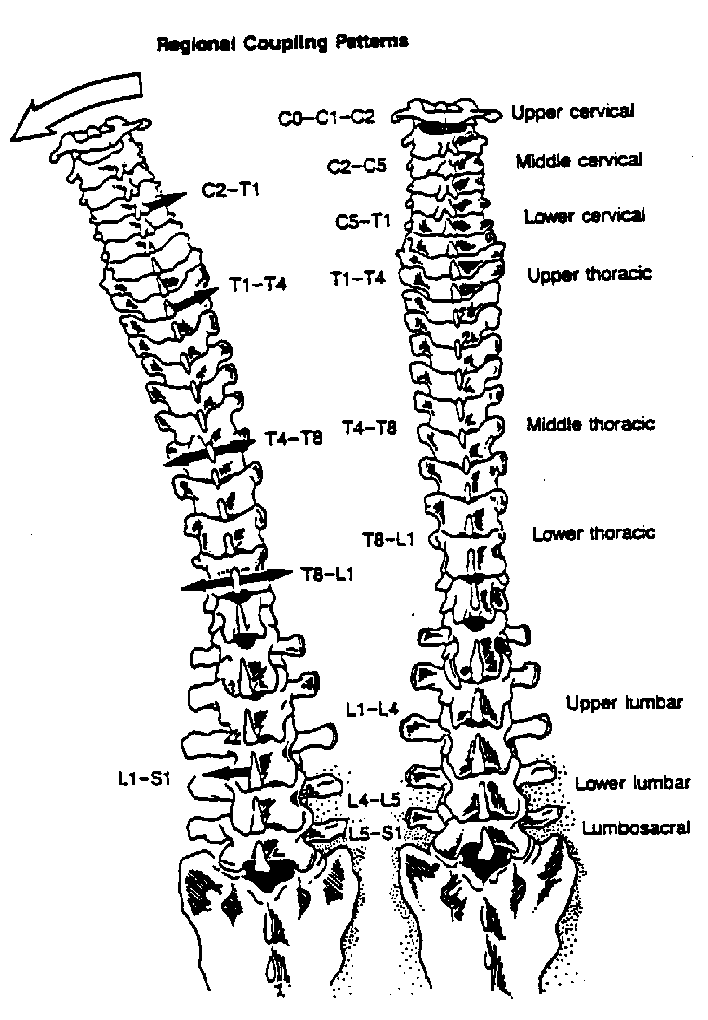
To continue to develop chiropractic clinical principles and skills relating to assessment of spinal health in an overall sense, including vertebral subluxation analysis and the development of psychomotor skills of adjustment procedures utilising toggle recoil and sustained impulse thrusts. NZCC vertebral subluxation analysis is a multi-test system. In this course students are introduced to four types of leg length evaluations, advanced muscle palpation, motion palpation, joint play and evaluation of the tone of the various types of paraspinal tissues.